La vergonha (Occitan for shame, pronounced [beɾˈɣuɲɔ]) is
what Occitans call the nefarious effects of various governmental
policies in France on French (in its broader sense) children and
citizens whose mother tongue was one of so-called patois — better
referred to as unofficial languages spoken within the French State, —
and langue d'oc in particular all across Occitania. Vergonha is being
made to reject and feel ashamed of one's (or one's parents') non-French
language through official exclusion, humiliation at school and/or media
ostracism as organized and sanctioned by French political leaders, from
Henri Grégoire to Nicolas Sarkozy. Vergonha, which is still a taboo
topic in France where some still refuse to admit such discrimination
ever existed, can be seen as the result of an attempted linguicide, as
hereafter developed.
1 Late 18th to late 19th century
1.1 The necessity to annihilate the patois
1.2 The end of traditional Occitan provinces
2 Policies and legacy of Jules Ferry
2.1 School humiliations
2.2 Role of the Church
3 Mid-20th century to the present
3.1 Constitutional issues
3.2 The Occitan legacy
Already in 1539 with Art. 111 of the Ordinance of Villers-Cotterêts, non-French languages in France were dealt a severe blow when it became compulsory "to deliver and execute all [legal] acts in the French language" (de prononcer et expedier tous actes en langaige françoys). Originally meant as a way to get rid of Latin in official documents — few 16th-century French subjects were educated and familiar with Latin, — it also stated that French and only French was to be made legal (en langage maternel françoys et non aultrement) in the kingdom.
But the deliberate process of eradicating non-French vernaculars in modern France and disparaging them as being but mere local and often strictly oral dialects, really started with Abbé Grégoire's Report on the necessity and means to annihilate the patois and to universalise the use of the French language, which he presented on June 4, 1794 to the National Convention and was followed by the official banning of all languages other than French in the administration and school for the sake of linguistically uniting post-Bastille Day France in a time when only one tenth of the population were fluent in French, that is to say around three million out of a total twenty-eight.
As for the very derogatory choice of the word "patois", which translates only partly to "dialect" in English, Jean Jaurès famously claimed that "one names patois the language of a defeated nation". According to the Chambers Dictionary, the origin of the term is disputed but could be a "corruption of patrois, from LL patriensis, a local inhabitant".
Four months earlier (January 27), Bertrand Barère de Vieuzac, despite being an Occitan from Tarbes himself, had claimed before this same Convention that

This ultra-republican policy is particularly obvious in the way France's inner borders were redesigned, thus creating 83 départements. The law was passed on December 22, 1789 and took effect the following year, on March 4, 1790. In the early 20th century, the départements were grouped into régions, to create a level of government between the departmental and national.
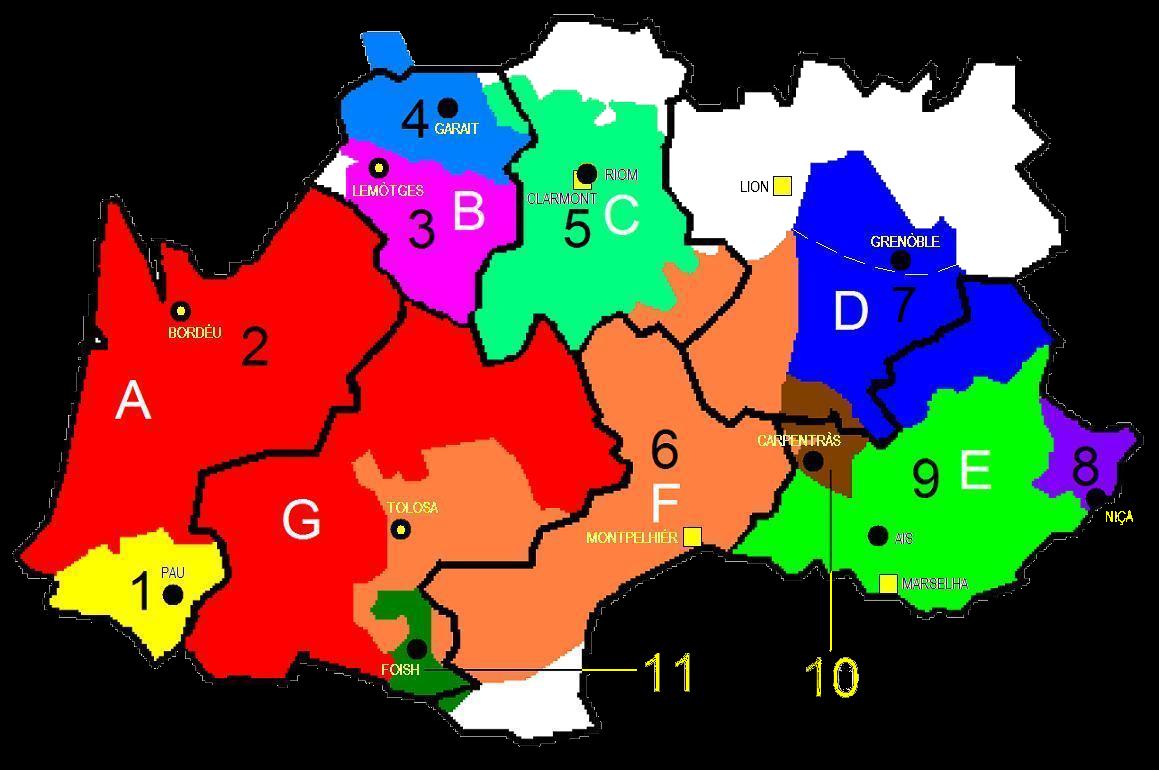
While the régions were intended to replace the old provinces, they were not necessarily formed along the same boundaries. As the map shows, there were eleven Occitan-speaking enclaves in the pre-1789 state, such as the powerful lands of Languedoc and Gascony, but they were divided into seven régions with no regard whatsoever for cultural and linguistic identities. This is how Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur was created out of portions of five Occitan provinces and three capitals were scrapped in favour of Marseille; and Auvergne came to comprise both native and Oïl-language entities. Meanwhile, the city of Nantes was administratively removed from Brittany, of which it had been one of two traditional capitals (along with Rennes), and the city of Toulouse was not included in the région of Languedoc-Rousillon, though it had historically been located in that province. Many of the régions contain hyphenated names, reflecting the merging of multiple historically distinction areas. This is true for four of the seven régions of Occitania: Languedoc-Roussillon, Midi-Pyrénées, Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur and Rhône-Alpes.
As a result, the centuries-old singularities of the various Occitan-speaking parts were overlooked and shaken in a deliberate effort by the newly-formed government to weaken and parcel out long-established feudal domains so that republican France would subdue traditional allegiances, as Antonin Perbòsc reveals in the Foreword to his Anthologie:
In short:
● Toulouse lost 76% of its territory of Languedoc
● Bordeaux lost a little more than half its territory of Gascony and Guyenne
● Limoges increased its administrative area by 43%
● Guéret, Pau, Foix, Riom, Aix-en-Provence, Grenoble, Carpentras (1791) and Nice (1860) lost their status as capitals
● Clermont-Ferrand, Montpellier and Marseille became capitals of Auvergne, Languedoc-Roussillon and Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur, respectively
● Languedoc was divided into five unequal parts, the largest of which forming Languedoc-Roussillon with the Catalan-speaking province of Roussillon
● The County of Marche, Béarn, the County of Foix and subsequently Comtat Venaissin and the County of Nice lost their autonomy
● Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur is made up of Provence and the County of Nice and bits and pieces of three other provinces
● The north of Languedoc and Comtat Venaissin and the western half of Dauphiné became linguistic minorities in the new Rhône-Alpes region
● The Occitan provinces spread over a little less than 200,000km², twice the area of South Korea and just over that of Senegal, more than twenty-three times the size of the island of Corsica
● The size of Gascony and Guyenne was comparable to that of Sierra Leone, Ireland, Georgia and Sri Lanka, or eight times the land area of Corsica
● The size of Languedoc was comparable to that of Denmark, Estonia and Bhutan, and over five times the size of Corsica
● Gascony and Guyenne, Languedoc, Provence and Auvergne accounted for 78.4% of Occitania in terms of land area, with Gascony and Guyenne making up for over a third of the total surface and Languedoc almost a quarter
In the 1880s, Jules Ferry implemented a series of strict measures to further weaken regional languages in France, as shown in Bernard Poignant's 1998 report to Lionel Jospin. These included children being given punishments by their teachers for speaking Occitan in a Toulouse school or Breton in Brittany. As Pêr-Jakez Helias (1914-1995), the author of the 1975 best-selling novel Le Cheval d'orgueil (The Horse of Pride), recalls in an interview:

Among other well-known humiliations was clogging young rebels, namely hanging a clog (sabot) around their necks as this young lady remembers her grandparents say:
This practice was referred to as le symbole by officials and la vache (the cow) by pupils with offenders becoming vachards. A whole range of objects were used, not just clogs: horseshoes, shingles, slates, wooden plates with a message, coins with a cross on them... The following are official instructions from a Finistère sub-prefect to teachers in 1845: "And remember, Gents: you were given your position in order to kill the Breton language." The prefect of Basses-Pyrénées in the French Basque Country wrote in 1846: "Our schools in the Basque Country are particularly meant to substitute the Basque language with French..."
Resorting to the practice of clogging is confirmed by the Autonomes de Solidarité Laïques website:
As for signs, they were also found in Poitou schools:
The Conselh de Representacion Generala de la Joventut d'Òc (CRGJOC, General Representation Council of the Occitan Youth), through the Youth of European Nationalities website, reports that
The Confolentés Occitan (Occitan-speaking Limousin) website testifies of the methods used by French authorities over the past century or so:
In the school of Camélas in Northern Catalonia, a former pupil reports,
As can be seen from these examples, Abbé Grégoire's own terms were kept to designate the languages of France: while Breton referred to the so-called dialect spoken in Brittany, the word patois encompassed all Romance dialects such as Occitan and Franco-Provençal. In his report, Corsican and Alsatian were dismissed as "highly degenerate" (très-dégénérés) forms of Italian and German, respectively. As a result, some people still call their non-French language patois, encouraged by the fact they were never taught how to write it and made to think only French exists in the written form.
In 1902, in a speech before the Conseil Général of Morbihan, Chief Education Officer Dantzer recommended that "the Church give first communion only to French-speaking children". In the same year, Émile Combes, then the President of the Council of Ministers of France and an Occitan, told the prefects of Morbihan, Côtes-du-Nord and Finistère that:
As Jaume Corbera Pou, a renowned Catalan linguist, argues,
In 1972, Georges Pompidou, the President of France and an Occitan, declared that "there is no room for regional languages in a France which fate is to mark Europe with its seal".
In a pre-election speech in Lorient, on March 14, 1981, François Mitterrand asserted that:
Unfortunately nothing was done.
In 1992, after some questioned the unconstitutional segregation of minority languages in France, Art. II of the 1958 French Constitution was revised so that "the language of the Republic shall be French" (la langue de la République est le français). This was achieved only months before the Council of Europe passed the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages, which Jacques Chirac ignored despite Lionel Jospin's plea for the Constitutional Council to amend Art. II and include all vernacular languages spoken on French soil. Yet again, non-French languages in France were denied official recognition and deemed too dangerous for the unity of the country, and Occitans, Basques, Corsicans, Catalans, Bretons, Alsatians etc have still no legal right to exist as such in their home lands. The text was again refused by right-wing majority deputies on January 18, 2008.
On the UMP website, Nicolas Sarkozy denies any mistreatment and even claims in a pre-electoral speech in Besançon on March 13, 2007 that
His Socialist rival, Ségolène Royal, on the contrary, declares herself ready to sign the Charter in a March 2007 speech in Iparralde for the sake of cultural variety in France:
Author Ives Roqueta writes about the shame of being Occitan in France in a text on the Aprene website:
Yet, the Occitan language is still alive, though official seclusion has had a devastating effect on the number of speakers in Occitania. Singer Patric alludes to this whole situation in a song called Soi un marrit dròlle (I'm a Bad Guy):
Claudi Martí questions the obscurantism in France's educational system in Perqué m'an pas dit? (Why Didn't They Tell Me?):
Joan Pau Verdier dedicates his song Veiquí l'occitan (This Is the Occitan) to fighting la vergonha and to the pride of being Occitans:
Jan dau Melhau, from Limousin, in Lo Diable es jos la pòrta (The Devil Lies Under the Door), tells how Occitans learned to feel ashamed of their occitanity in a society that denied them any legitimity:
Hartèra (Enough!), a youth movement for the promotion of Occitan, militates against the shaming, as can be seen on this poster. It reads in both Gascon Occitan and French, with a touch of irony and a renewed confidence in the future of Occitania:

To hell with the shame...
Our patois is a language: Occitan;
Our South is a country: Occitania;
Our folklore is a culture.
We want respect for our difference.
Share, mix, walk!!
1 Late 18th to late 19th century

1.1 The necessity to annihilate the patois
1.2 The end of traditional Occitan provinces
2 Policies and legacy of Jules Ferry

2.1 School humiliations
2.2 Role of the Church
3 Mid-20th century to the present

3.1 Constitutional issues
3.2 The Occitan legacy
Already in 1539 with Art. 111 of the Ordinance of Villers-Cotterêts, non-French languages in France were dealt a severe blow when it became compulsory "to deliver and execute all [legal] acts in the French language" (de prononcer et expedier tous actes en langaige françoys). Originally meant as a way to get rid of Latin in official documents — few 16th-century French subjects were educated and familiar with Latin, — it also stated that French and only French was to be made legal (en langage maternel françoys et non aultrement) in the kingdom.
| LATE 18TH TO LATE 19TH CENTURY |
| The necessity to annihilate the patois |
But the deliberate process of eradicating non-French vernaculars in modern France and disparaging them as being but mere local and often strictly oral dialects, really started with Abbé Grégoire's Report on the necessity and means to annihilate the patois and to universalise the use of the French language, which he presented on June 4, 1794 to the National Convention and was followed by the official banning of all languages other than French in the administration and school for the sake of linguistically uniting post-Bastille Day France in a time when only one tenth of the population were fluent in French, that is to say around three million out of a total twenty-eight.
As for the very derogatory choice of the word "patois", which translates only partly to "dialect" in English, Jean Jaurès famously claimed that "one names patois the language of a defeated nation". According to the Chambers Dictionary, the origin of the term is disputed but could be a "corruption of patrois, from LL patriensis, a local inhabitant".
Four months earlier (January 27), Bertrand Barère de Vieuzac, despite being an Occitan from Tarbes himself, had claimed before this same Convention that
The monarchy
had reasons to resemble the Tower of Babel; in democracy, leaving the
citizens to ignore the national language [that of Paris], unable to
control the power, is betraying the motherland... For a free people,
the tongue must be one and the same for everyone. [...] How much money
have we not spent already for the translation of the laws of the first
two national assemblies in the various dialects of France! As if it
were our duty to maintain those barbaric jargons and those coarse
lingos that can only serve fanatics and counter-revolutionaries now!

| The end of traditional Occitan provinces |
This ultra-republican policy is particularly obvious in the way France's inner borders were redesigned, thus creating 83 départements. The law was passed on December 22, 1789 and took effect the following year, on March 4, 1790. In the early 20th century, the départements were grouped into régions, to create a level of government between the departmental and national.
While the régions were intended to replace the old provinces, they were not necessarily formed along the same boundaries. As the map shows, there were eleven Occitan-speaking enclaves in the pre-1789 state, such as the powerful lands of Languedoc and Gascony, but they were divided into seven régions with no regard whatsoever for cultural and linguistic identities. This is how Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur was created out of portions of five Occitan provinces and three capitals were scrapped in favour of Marseille; and Auvergne came to comprise both native and Oïl-language entities. Meanwhile, the city of Nantes was administratively removed from Brittany, of which it had been one of two traditional capitals (along with Rennes), and the city of Toulouse was not included in the région of Languedoc-Rousillon, though it had historically been located in that province. Many of the régions contain hyphenated names, reflecting the merging of multiple historically distinction areas. This is true for four of the seven régions of Occitania: Languedoc-Roussillon, Midi-Pyrénées, Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur and Rhône-Alpes.

| Traditional Occitan
provinces:
1. Béarn (Pau) — 6,800km² (est.) 2. Guyenne & Gascony (Bordeaux) — 69,400km² (est.) 3. Limousin (Limoges) — 9,700km² (est.) 4. County of Marche (Guéret) — 7,600km² (est.) 5. Auvergne (Riom) — 19,300km² (est.) 6. Languedoc (Toulouse) — 45,300km² (est.) 7. Dauphiné (Grenoble) — 8,500km² (est.) 8. County of Nice — 3,600km² (est.) 9. Provence (Aix-en-Provence) — 22,700km² (est.) 10. Comtat Venaissin (Carpentras) — 3,600km² (est.) 11. County of Foix (Foix) — 3,300km² (est.) | Régions of France:
A. Aquitaine (Bordeaux) — 41,308km² B. Limousin (Limoges) — 16,942km² C. Auvergne (Clermont-Ferrand) — 26,013km² D. Rhône-Alpes (Lyon) — 43,698km² E. Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur (Marseille) — 31,400km² F. Languedoc-Roussillon (Montpellier) — 27,376km² G. Midi-Pyrénées (Toulouse) — 45,348km² - - -: Occitan / Franco-Provençal linguistic limit |
As a result, the centuries-old singularities of the various Occitan-speaking parts were overlooked and shaken in a deliberate effort by the newly-formed government to weaken and parcel out long-established feudal domains so that republican France would subdue traditional allegiances, as Antonin Perbòsc reveals in the Foreword to his Anthologie:
When the
Constituante created the départements, their goal was clearly to erase
the old geographical and historical distinction of the provinces;
however this goal was not as perfectly met as some would have liked: in
general, the départements were made up of pieces of existing provinces,
quite seldom of the reunion of parts from different provinces. If one
could criticize this territorial division for being too arbitrary and
too geometric, what can be said of Tarn-et-Garonne, born of a
sénatus-consule [a
law by the Senate of France]
on November
2, 1808? Of
course, one may think that the Centralisateur [Napoleon I
of France]
felt real pleasure showing he could do even better than the
centralisateurs of the National Constituent Assembly. With fragments of
Quercy, Rouergue, Agenais, Lomagne, Gascony and Languedoc, creating a
new unit so little vast and yet so diverse of soil, language and race,
what a great idea! And maybe the audacious half-god had only one
regret: coming a little too late to redesign according to this pattern
all the provinces of old France...
In short:
● Toulouse lost 76% of its territory of Languedoc
● Bordeaux lost a little more than half its territory of Gascony and Guyenne
● Limoges increased its administrative area by 43%
● Guéret, Pau, Foix, Riom, Aix-en-Provence, Grenoble, Carpentras (1791) and Nice (1860) lost their status as capitals
● Clermont-Ferrand, Montpellier and Marseille became capitals of Auvergne, Languedoc-Roussillon and Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur, respectively
● Languedoc was divided into five unequal parts, the largest of which forming Languedoc-Roussillon with the Catalan-speaking province of Roussillon
● The County of Marche, Béarn, the County of Foix and subsequently Comtat Venaissin and the County of Nice lost their autonomy
● Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur is made up of Provence and the County of Nice and bits and pieces of three other provinces
● The north of Languedoc and Comtat Venaissin and the western half of Dauphiné became linguistic minorities in the new Rhône-Alpes region
● The Occitan provinces spread over a little less than 200,000km², twice the area of South Korea and just over that of Senegal, more than twenty-three times the size of the island of Corsica
● The size of Gascony and Guyenne was comparable to that of Sierra Leone, Ireland, Georgia and Sri Lanka, or eight times the land area of Corsica
● The size of Languedoc was comparable to that of Denmark, Estonia and Bhutan, and over five times the size of Corsica
● Gascony and Guyenne, Languedoc, Provence and Auvergne accounted for 78.4% of Occitania in terms of land area, with Gascony and Guyenne making up for over a third of the total surface and Languedoc almost a quarter
| POLICIES AND LEGACY OF JULES FERRY |
| School humiliations |
In the 1880s, Jules Ferry implemented a series of strict measures to further weaken regional languages in France, as shown in Bernard Poignant's 1998 report to Lionel Jospin. These included children being given punishments by their teachers for speaking Occitan in a Toulouse school or Breton in Brittany. As Pêr-Jakez Helias (1914-1995), the author of the 1975 best-selling novel Le Cheval d'orgueil (The Horse of Pride), recalls in an interview:
Now I know, I learned that there
was a government policy which goal was
obviously to make France one and indivisible, and as a result regional
languages had to disappear. But I didn't know it then and maybe the
teachers of the Third Republic did, though I asked some of them and
they all denied it. Their own job was to teach us French. And
consequently, while attending school, we were required to speak French.
Whenever we used Breton instead, we weren't doing our share and so we
deserved to be expelled. Period.

Among other well-known humiliations was clogging young rebels, namely hanging a clog (sabot) around their necks as this young lady remembers her grandparents say:
My grandparents speak Breton
too, though not with me. As children, they
used to have their fingers smacked [with a stick or ruler] if they
happened to say a word in Breton. Back then, the French of the
Republic, one and indivisible, was to be heard in all schools and those
who dared challenge this policy were humiliated with having to wear a
clog around their necks or kneel down on a ruler under a sign that
read: "It is forbidden to spit on the ground and speak
Breton".
That's the reason why some older folks won't transmit the language to
their children: it brings trouble upon yourself...
This practice was referred to as le symbole by officials and la vache (the cow) by pupils with offenders becoming vachards. A whole range of objects were used, not just clogs: horseshoes, shingles, slates, wooden plates with a message, coins with a cross on them... The following are official instructions from a Finistère sub-prefect to teachers in 1845: "And remember, Gents: you were given your position in order to kill the Breton language." The prefect of Basses-Pyrénées in the French Basque Country wrote in 1846: "Our schools in the Basque Country are particularly meant to substitute the Basque language with French..."
Resorting to the practice of clogging is confirmed by the Autonomes de Solidarité Laïques website:
School has had a unifying role
inasmuch as speaking the "noble"
language [French]
reduced the use of regional dialects and patois. Let
us mention the humiliation of children made to wear a clog around their
necks for inadvertently speaking a word in the language of the people.
As for signs, they were also found in Poitou schools:
It seems as though Jules Ferry
making school free and compulsory in
1881 materialized the work started four centuries earlier [with
the
Ordinance of Villers-Cotterêts];
the method of repression and
humiliation that was undertaken bore fruit with, for instance, the
famous signs in school reading: "It is forbidden to spit
on the ground
and speak patois."
The Conselh de Representacion Generala de la Joventut d'Òc (CRGJOC, General Representation Council of the Occitan Youth), through the Youth of European Nationalities website, reports that
Our language [Occitan] lost its name, becoming some
"patois", first at
school and then in families through putting pressure on women in
education ("Interdit de cracher par terre et de parler
patois") with
the French IIIrd Republic, Mussolini and Franco.
The Confolentés Occitan (Occitan-speaking Limousin) website testifies of the methods used by French authorities over the past century or so:
To help efface traditional
regional identities, the Occitan language
was not merely discouraged but actively suppressed. School pupils were
punished well within living memory for speaking their native language
on school premises. The French administration managed to make the
Occitan speakers think of their own language as a patois, i.e. as a
corrupted form of French used only by the ignorant and uneducated. This
alienating process is known as la vergonha ("the shame"). Many older
speakers of Occitan still believe that their native language is no more
than a shameful patois. This is one reason why you rarely hear it in
public — or anywhere outside of the neighbourhood or family circle.
In the school of Camélas in Northern Catalonia, a former pupil reports,
Everyone but the teacher's
children spoke Catalan among themselves.
We'd even get punished for that, because at the time, we all had to
speak French. Be Clean, Speak French could be found written on the
school's walls. And if you refused to speak French, they'd give you
some sort of wooden sign to wear until death came, as we said, which
meant the last offender, in the evening, had twenty lines to copy. We'd
speak French in the schoolyard, and for the first ten metres of the way
back home, for as long as we thought the teacher would overhear us, and
then we'd switch back to our own mother tongue, Catalan.
In those times, Catalan speakers were rather despised. My generation
associated speaking Catalan with a disadvantage, with being less than
the others, with running the risk of being left behind on the social
ladder, in short with bringing trouble.
As can be seen from these examples, Abbé Grégoire's own terms were kept to designate the languages of France: while Breton referred to the so-called dialect spoken in Brittany, the word patois encompassed all Romance dialects such as Occitan and Franco-Provençal. In his report, Corsican and Alsatian were dismissed as "highly degenerate" (très-dégénérés) forms of Italian and German, respectively. As a result, some people still call their non-French language patois, encouraged by the fact they were never taught how to write it and made to think only French exists in the written form.
| Role of the Church |
In 1902, in a speech before the Conseil Général of Morbihan, Chief Education Officer Dantzer recommended that "the Church give first communion only to French-speaking children". In the same year, Émile Combes, then the President of the Council of Ministers of France and an Occitan, told the prefects of Morbihan, Côtes-du-Nord and Finistère that:
Breton priests want to keep
their flock in ignorance by refusing to
promote education and using only the Breton language in religious
teachings and catechism. The Bretons will only be part of the Republic
the day they start speaking French.
| MID-20TH CENTURY TO THE PRESENT |
As Jaume Corbera Pou, a renowned Catalan linguist, argues,
When at the mid-19th century,
primary school is made compulsory all
across the State, it is also made clear that only French will be
taught, and the teachers will severely punish any pupil speaking in
patois. The aim of the French educational system will consequently not
be to dignify the pupils' natural humanity, developing their culture
and teaching them to write their language, but rather to humiliate them
and morally degrade them for the simple fact of being what tradition
and their nature made them. The self-proclaimed country of the "Human
rights" will then ignore one of man's most fundamental rights, the
right to be himself and speak the language of his nation. And with that
attitude France, the grande France that calls itself the champion
of
liberty, will pass the 20th century, indifferent to the timid protest
movements of the various linguistic communities it submitted and the
literary prestige they may have given birth to.
[...]
France, that under Franco's reign was seen here [in Catalonia] as the safe haven of freedom, has the miserable honour of being the State of Europe — and probably the world — that succeeded best in the diabolical task of destroying its own ethnic and linguistic patrimony and moreover, of destroying human family bonds: many parents and children, or grandparents and grandchildren, have different languages, and the latter feel ashamed of the first because they speak a despicable patois, and no element of the grandparents' culture has been transmitted to the younger generation, as if they were born out of a completely new world. This is the French State that has just entered the 21st century, a country where stone monuments and natural landscapes are preserved and respected, but where many centuries of popular creation expressed in different tongues are on the brink of extinction. The gloire and the grandeur built on a genocide. No liberty, no equality, no fraternity: just cultural extermination, this is the real motto of the French Republic.
France, that under Franco's reign was seen here [in Catalonia] as the safe haven of freedom, has the miserable honour of being the State of Europe — and probably the world — that succeeded best in the diabolical task of destroying its own ethnic and linguistic patrimony and moreover, of destroying human family bonds: many parents and children, or grandparents and grandchildren, have different languages, and the latter feel ashamed of the first because they speak a despicable patois, and no element of the grandparents' culture has been transmitted to the younger generation, as if they were born out of a completely new world. This is the French State that has just entered the 21st century, a country where stone monuments and natural landscapes are preserved and respected, but where many centuries of popular creation expressed in different tongues are on the brink of extinction. The gloire and the grandeur built on a genocide. No liberty, no equality, no fraternity: just cultural extermination, this is the real motto of the French Republic.
| Constitutional issues |
In 1972, Georges Pompidou, the President of France and an Occitan, declared that "there is no room for regional languages in a France which fate is to mark Europe with its seal".
In a pre-election speech in Lorient, on March 14, 1981, François Mitterrand asserted that:
The time has come to give the
languages and cultures of France an
official status. The time has come to open school doors wide for them,
to create regional radio and TV stations to let them be broadcast, to
ensure they play all the role they deserve in public life.
Unfortunately nothing was done.
In 1992, after some questioned the unconstitutional segregation of minority languages in France, Art. II of the 1958 French Constitution was revised so that "the language of the Republic shall be French" (la langue de la République est le français). This was achieved only months before the Council of Europe passed the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages, which Jacques Chirac ignored despite Lionel Jospin's plea for the Constitutional Council to amend Art. II and include all vernacular languages spoken on French soil. Yet again, non-French languages in France were denied official recognition and deemed too dangerous for the unity of the country, and Occitans, Basques, Corsicans, Catalans, Bretons, Alsatians etc have still no legal right to exist as such in their home lands. The text was again refused by right-wing majority deputies on January 18, 2008.
On the UMP website, Nicolas Sarkozy denies any mistreatment and even claims in a pre-electoral speech in Besançon on March 13, 2007 that
If I'm
elected, I won't be in favour of the European Charter for
Regional Languages. I don't want that tomorrow a judge with a
historical experience of the issue of minorities different from ours,
decides that a regional language must be considered as a language of
the Republic just like French. Because, beyond the text itself, there
is a dynamic of interpretations and jurisprudence that can go very far.
I am convinced that in France, the land of the free, no minority is
discriminated against and consequently it is not necessary to grant
European judges the right to give their opinion on a matter that is
consubstantial with our national identity and has absolutely nothing to
do with the construction of Europe.
His Socialist rival, Ségolène Royal, on the contrary, declares herself ready to sign the Charter in a March 2007 speech in Iparralde for the sake of cultural variety in France:
Regional identities represent a
tremendous asset for the future and I
believe that understanding the link between the fundamental values that
make the deep-rooted identity between France and the French nation in
its diversity, in its authenticity, in its authentic traditions [...]
makes the State work well.
| The Occitan legacy |
Author Ives Roqueta writes about the shame of being Occitan in France in a text on the Aprene website:
The red is whirling in my mind,
I'm red with anger, red is my
rebellion. I'm red, the wine spilled over me, on the Corbières paths.
The red is confining my mind, I'm red with shame: I speak Occitan. I'm
red, red from the blood in my face. Wake up! Where is the blood of our
fathers?
Yet, the Occitan language is still alive, though official seclusion has had a devastating effect on the number of speakers in Occitania. Singer Patric alludes to this whole situation in a song called Soi un marrit dròlle (I'm a Bad Guy):
I'm a bad guy for killing your
language
But I'll make a much nicer, much better one for you
And when we only speak Occitan
We'll make love with a song
Farewell shame, I'm married now
With this girl I have many children
And we'll make men out of this country
Farewell shame, I am no outlaw! [...]
Farewell, o my land; welcome, o my home!
But I'll make a much nicer, much better one for you
And when we only speak Occitan
We'll make love with a song
Farewell shame, I'm married now
With this girl I have many children
And we'll make men out of this country
Farewell shame, I am no outlaw! [...]
Farewell, o my land; welcome, o my home!
Claudi Martí questions the obscurantism in France's educational system in Perqué m'an pas dit? (Why Didn't They Tell Me?):
As every child, I went to
school;
As every child, they taught me to read,
They sang me many songs, taught me so many stories: Lutetia... Paris... Paris...
But why, o why didn't they tell me the name of my language at school?
Our teacher would tell us about that great king of France
Kneeling down in front of the poor: a real saint, that saint Louis!
He loved each and every one and fought poverty: a real saint, that saint Louis!
But why, o why didn't they tell me at school that he killed my country?
And as we grew up, we had to speak three languages;
To make a good technician, you needed three languages,
And English and German and what they write in Rome to make a good technician.
But why, o why didn't they tell me the name of my language at school?
Maybe so much knowledge is hiding the truth from our eyes;
We'll learn by ourselves that freedom doesn't rule on earth;
We'll learn about the starvation in India and the mourning of Africans and the death of Che Guevara,
And why, yes why they didn't say the name of our country at school...
As every child, they taught me to read,
They sang me many songs, taught me so many stories: Lutetia... Paris... Paris...
But why, o why didn't they tell me the name of my language at school?
Our teacher would tell us about that great king of France
Kneeling down in front of the poor: a real saint, that saint Louis!
He loved each and every one and fought poverty: a real saint, that saint Louis!
But why, o why didn't they tell me at school that he killed my country?
And as we grew up, we had to speak three languages;
To make a good technician, you needed three languages,
And English and German and what they write in Rome to make a good technician.
But why, o why didn't they tell me the name of my language at school?
Maybe so much knowledge is hiding the truth from our eyes;
We'll learn by ourselves that freedom doesn't rule on earth;
We'll learn about the starvation in India and the mourning of Africans and the death of Che Guevara,
And why, yes why they didn't say the name of our country at school...
Joan Pau Verdier dedicates his song Veiquí l'occitan (This Is the Occitan) to fighting la vergonha and to the pride of being Occitans:
There was shame in the heart of
the land. We had lost the soil, the
trees were all dead, slaves in our own country, living a life of bowing
down, with no eyes or memory, a rogue nation.
You would tell me: "It's all over!" you my father and you my friends, "There's no coming back now". You'd say: "We must stop dreaming!"
Here comes hope at the end of the road. The new man is standing up. This is the Occitan. The rumour spreads to the smallest towns. We'll keep our land, we will not die!
We were born on a windy day when evil was blowing hard. We're through with being dogs. You see, Father, we aren't dead yet!
I greet you, Brother. Good morning, Farmer. A worker is calling you: another Occitan! Nothing's impossible anymore: we believe in love! And we believe our history is made of the future!
And, Mother, I see you today. Springtime blossoms in your hair. You've understood our sun. You perfectly know we aren't crazy.
Here comes the hope. May the child sing. We'll have a right to live, to be Occitans. I greet you, Brother; good morning, Farmer! The new man is calling you, he's a Basque, a Breton...
You would tell me: "It's all over!" you my father and you my friends, "There's no coming back now". You'd say: "We must stop dreaming!"
Here comes hope at the end of the road. The new man is standing up. This is the Occitan. The rumour spreads to the smallest towns. We'll keep our land, we will not die!
We were born on a windy day when evil was blowing hard. We're through with being dogs. You see, Father, we aren't dead yet!
I greet you, Brother. Good morning, Farmer. A worker is calling you: another Occitan! Nothing's impossible anymore: we believe in love! And we believe our history is made of the future!
And, Mother, I see you today. Springtime blossoms in your hair. You've understood our sun. You perfectly know we aren't crazy.
Here comes the hope. May the child sing. We'll have a right to live, to be Occitans. I greet you, Brother; good morning, Farmer! The new man is calling you, he's a Basque, a Breton...
Jan dau Melhau, from Limousin, in Lo Diable es jos la pòrta (The Devil Lies Under the Door), tells how Occitans learned to feel ashamed of their occitanity in a society that denied them any legitimity:
There came a time when people
felt ashamed:
They felt ashamed of what they spoke;
Of their language mended with the thread of such a long history, they felt ashamed.
There came a time when people felt ashamed:
They felt ashamed of how they spoke;
Of saying so much in so little and making their minds smile, they felt ashamed. [...]
There came a time when people felt ashamed:
They felt ashamed of what they were;
Of what had made them what they were, they felt ashamed.
Cursed be the time when people felt ashamed
And cursed be those who let themselves feel ashamed!
They felt ashamed of what they spoke;
Of their language mended with the thread of such a long history, they felt ashamed.
There came a time when people felt ashamed:
They felt ashamed of how they spoke;
Of saying so much in so little and making their minds smile, they felt ashamed. [...]
There came a time when people felt ashamed:
They felt ashamed of what they were;
Of what had made them what they were, they felt ashamed.
Cursed be the time when people felt ashamed
And cursed be those who let themselves feel ashamed!
Hartèra (Enough!), a youth movement for the promotion of Occitan, militates against the shaming, as can be seen on this poster. It reads in both Gascon Occitan and French, with a touch of irony and a renewed confidence in the future of Occitania:

To hell with the shame...
Our patois is a language: Occitan;
Our South is a country: Occitania;
Our folklore is a culture.
We want respect for our difference.
Share, mix, walk!!